Investors and traders, especially those dealing with volatile securities like penny stocks, often struggle with the concept of stop-loss orders. These issues are common among Reddit communities like r/pennystocks, where users frequently share their experiences and concerns about stop-loss strategies. For example, one user lamented missing their stop-loss execution due to sudden price spikes or drops, a common occurrence in volatile markets. This happens because market conditions can shift rapidly, rendering traditional stop-loss strategies ineffective.
This is where a trailing stop loss can provide a flexible solution. By dynamically adjusting the stop-loss level based on a stock’s movement, it allows investors to lock in profits while limiting losses, making it a preferred tool for managing risk in volatile markets.
Types of Stop Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are essential risk management tools used to limit losses and secure gains. Here are the primary types:
| Type of Stop Loss | Description | Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Stop Loss | Set at a specific price below (or above, for short selling) the purchase price. | Best for stable stocks with less volatility. | Purchased at $100, fixed stop loss set at $95. |
| Percentage-Based Stop Loss | Determined as a percentage of the purchase price. | Balances risk-reward ratio for traders. | 10% stop loss on $100 stock triggers at $90. |
| Trailing Stop Loss | Dynamically adjusts with the stock price, maintaining a predefined percentage or dollar gap. | Ideal for volatile markets or penny stocks. | 5% trailing stop on $100 stock adjusts to $104.50 when price rises to $110. |
| Time-Based Stop Loss | Activates at a specific time regardless of price movements. | Useful for traders with defined timeframes. | Day trader sets stop loss to trigger at 3:45 PM if a level isn’t reached. |
| Stop-Limit Orders | Combines stop-loss and limit orders, setting a price range for selling. | For controlling exact selling price but risks no execution in rapid drops. | Set stop at $95 and limit at $93 for |
What is a Trailing Stop Loss?
A trailing stop loss is an advanced trading tool designed to protect profits and minimize losses by dynamically adjusting its level based on the movement of a security’s price. Unlike a fixed stop-loss order, which remains static regardless of price fluctuations, a trailing stop follows the price of a stock upward (or downward for short selling) and locks in gains as the price moves in your favor.
This approach is especially effective in volatile markets or with assets prone to rapid price swings, like penny stocks. Many traders on platforms like Reddit’s r/pennystocks often voice concerns about the limitations of traditional stop-loss orders. For example, a user might set a fixed stop loss but miss opportunities for greater profits due to sudden spikes. A trailing stop solves this by adjusting automatically as the stock rises, ensuring flexibility and better control.
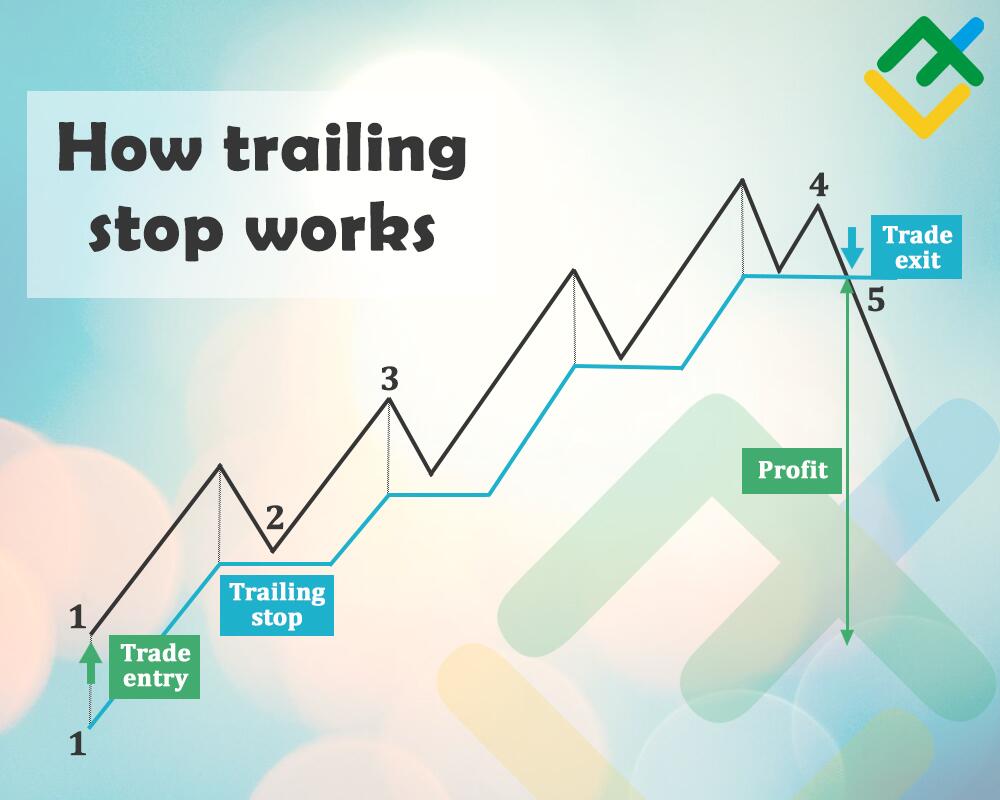
How It Works
Two Primary Mechanisms:
- Percentage-Based Trailing Stop
- The stop-loss level follows the stock price at a fixed percentage.
- Example: If you set a 10% trailing stop on a $100 stock, the stop is initially placed at $90. If the stock price rises to $110, the stop adjusts to $99. If the stock falls below $99, the order triggers and sells the stock.
- Dollar-Based Trailing Stop
- Instead of a percentage, the stop-loss adjusts based on a fixed dollar amount.
- Example: If you set a $10 trailing stop on a $100 stock, the stop is set at $90. If the stock moves to $120, the stop rises to $110. However, if the stock drops to $110, the trailing stop remains fixed and triggers the sale.
Key Feature: The trailing stop only moves in one direction—up for long positions and down for short positions. If the stock’s price reverses and hits the trailing stop, the order executes and prevents further losses or locks in profits.
How to Set a Trailing Stop Loss
Setting up a trailing stop loss requires careful planning to align it with your risk tolerance, trading strategy, and the asset’s volatility. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Determine the Type of Trailing Stop Loss
Decide whether to use a percentage-based or dollar-based trailing stop.
- Use percentage-based stops for long-term investments and volatile assets.
- Use dollar-based stops for assets with less price movement or shorter holding periods.
2. Choose the Trailing Stop Level
The stop level is critical in striking a balance between protecting gains and giving the trade room to move.
- For Stable Assets: Use a tighter stop, like 5%, to minimize losses.
- For Volatile Assets: Use a wider stop, like 10%-15%, to avoid premature triggers.
3. Set the Order in Your Trading Platform
Most trading platforms have built-in tools to set trailing stop orders.
- Locate the “Trailing Stop” option under order types.
- Enter the percentage or dollar amount you wish to trail the stock by.
- Review the order details before submitting.
4. Monitor Market Conditions
While trailing stops automate risk management, sudden price gaps or market volatility can lead to execution at less-than-ideal levels.
- Keep an eye on major market events, earnings reports, or announcements that could impact price movements.
5. Adjust the Trailing Stop Periodically
As your portfolio grows or your strategy evolves, reassess and fine-tune your trailing stop settings.
- Tighten stops to secure profits when approaching a price target.
- Widen stops to accommodate expected volatility during news events or earnings season.
Example of Setting a Trailing Stop Loss
| Scenario | Price Movement | Trailing Stop Level | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Buy Price | $100 | $90 (10% trailing stop) | Position established |
| Stock Rises to $120 | Adjusts to $108 | Stop locks in profit | |
| Stock Falls to $110 | Remains at $108 | Stop holds position | |
| Stock Falls to $108 | Triggers sell order | Trade exits, $8 profit |
Benefits of Using Trailing Stop Loss
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Protects Against Losses | Automatically limits downside risk when the price drops significantly. |
| Locks in Gains | Moves with the stock price, ensuring profits are preserved as the price rises. |
| Reduces Emotional Decisions | Automates trading, minimizing impulsive reactions to market fluctuations. |
| Adapts to Market Movements | Adjusts dynamically to price changes, providing flexibility in volatile conditions. |
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Premature triggering in volatility | Set a wider trailing stop level for high-volatility stocks. |
| Gaps in market prices | Consider combining trailing stops with limit orders to manage gaps effectively. |
| Over-reliance on automation | Regularly review stop-loss settings and market conditions to ensure alignment with goals. |
By carefully setting up a trailing stop loss, traders can confidently navigate market uncertainties, lock in profits, and minimize losses without constant monitoring.
Related articles:
10 Best Penny Stocks Of 2025, which is up 25% in January
Lessons learned: After making $20K from penny stocks and losing it all
Common Mistakes People Make When Investing and How to Avoid Them
Behaviors That Prevent Smart Investing Decisions and How to Overcome Them
How to Get a Startup Business Loan with No Money Online: A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Invest in Gold and Silver: A Step-by-Step Guide
How To Invest $1,000 And Grow Your Money in 2025
CD vs. mutual fund: Which is a better investment?
Sources:
Investopedia – Stop Loss Orders










