If you’re wondering what is stock market, it refers to the collection of markets where stocks (shares of ownership in publicly traded companies) are bought and sold. The stock market plays a crucial role in the economy by enabling businesses to raise capital and allowing investors to earn a return on their investments.
What Is Stock Market?
At its core, the stock market is a marketplace where investors can buy and sell shares of companies. These shares represent ownership in a corporation, and buying a share gives you a stake in that company’s earnings and assets. The stock market is divided into different exchanges, such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Nasdaq, where most stock transactions take place.
| Exchange | Location | Market Cap ($ billions) |
|---|---|---|
| NASDAQ | U.S. | $25.00 |
| NYSE | U.S. | 24.9 |
| Euronext | Europe | 6.6 |
| Shanghai Stock Exchange | China | 6.5 |
| Tokyo Stock Exchange | Japan | 6.5 |
| India National Stock Exchange | India | 4.6 |
| Shenzhen Stock Exchange | China | 4.0 |
| Hong Kong Stock Exchange | Hong Kong | 3.8 |
| London Stock Exchange | U.K. | 3.4 |
| Toronto Stock Exchange (TMX) | Canada | 3.1 |
| Saudi Stock Exchange (Tadawul) | Saudi Arabia | 3.0 |
- Primary Market: In the primary market, companies issue new stocks to raise capital, typically through an Initial Public Offering (IPO). This is the first time shares are made available to the public.
- Secondary Market: After the IPO, stocks are traded among investors in the secondary market. This is what most people refer to as the stock market, where buyers and sellers exchange existing shares through stock exchanges like the NYSE or Nasdaq.

How the Stock Market Works
To understand what is stock market and how it works, you need to know how buying and selling stocks take place, who the key players are, and what factors influence stock prices.
- Buyers and Sellers: The stock market functions as an auction system where buyers and sellers negotiate the price of stocks. If a buyer is willing to pay the price a seller asks, the transaction is completed, and ownership of the shares is transferred.
- Stock Prices: Stock prices fluctuate based on supply and demand. When more people want to buy a stock than sell it, the price rises. Conversely, when more people want to sell than buy, the price drops. Factors such as company performance, economic conditions, and investor sentiment all influence stock prices.
- Brokers and Trading Platforms: To buy and sell stocks, investors typically use brokers or online trading platforms like E*TRADE or TD Ameritrade. These brokers act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, executing trades on your behalf for a fee.
What Is Stock Market And What Is Sold in it?
While the stock market is best known for trading company stocks, many other assets are traded as well, providing investors with various options to diversify their portfolios.
- Stocks: Shares of publicly traded companies are the primary assets traded. When you buy stock, you’re purchasing a small ownership stake in that company. Stocks are bought and sold through stock exchanges like the NYSE and Nasdaq.
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities issued by corporations, municipalities, or governments. When you buy a bond, you’re essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the bond’s face value at maturity.
- Commodities: Physical assets like gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products can be traded in the stock market. Commodities are typically traded through futures contracts, allowing investors to speculate on the price of these goods.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs are baskets of securities that track an index, commodity, or sector. They are traded like stocks on an exchange and provide investors with diversification in a single product.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds pool money from many investors to buy a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They are managed by professional fund managers and offer diversification for investors.
- Options: Options give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a stock at a specific price before a certain date. These are more complex financial instruments and are typically used for hedging or speculative purposes.
The Role of Stock Exchanges and Indexes
Understanding what is stock market also involves knowing about stock exchanges and indexes that help investors track market performance.
- Stock Exchanges: Stock exchanges, such as the NYSE and Nasdaq, are physical or digital marketplaces where stocks are traded. Each exchange has its own listing requirements, and companies must meet these standards to be traded on a particular exchange.
- Market Indexes: Stock market indexes like the S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average are benchmarks that track the performance of a group of stocks. These indexes help investors gauge the health of the overall market. For example, the S&P 500 tracks the top 500 companies in the U.S. and is often seen as a broad measure of the stock market’s performance.

How Stock Prices Are Determined
Stock prices fluctuate based on supply and demand, but several underlying factors drive these market dynamics.
- Supply and Demand: At the most basic level, stock prices are determined by the balance between supply (shares available for sale) and demand (the number of people wanting to buy). If more investors are interested in buying a stock than selling, the price will rise. Conversely, if more people want to sell, the price will drop.
- Company Performance: A company’s financial health, profitability, and growth potential are significant factors influencing its stock price. Positive earnings reports or news about product launches often lead to price increases, while poor financial performance can cause prices to fall.
- Economic Indicators: Economic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and GDP growth also affect stock prices. For example, when interest rates are low, borrowing is cheaper, which can lead to increased business investment and higher stock prices.
- Investor Sentiment: Stock prices are not just influenced by financials but also by investor psychology. Fear and greed can cause short-term price fluctuations, as investors react to news or market trends with emotional buying and selling.
- Market News: News about the company or industry can also have an immediate impact on stock prices. For example, announcements of mergers, acquisitions, or changes in leadership can move stock prices in either direction depending on investor interpretation.
The Role of Brokers and Market Makers
Brokers and market makers play critical roles in ensuring that the stock market operates smoothly.
- Brokers: Brokers act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers. When you place an order to buy or sell stock, your broker facilitates that trade for a commission or fee. With the rise of online platforms, brokers like Robinhood and E*TRADE make it easy for individuals to participate in the stock market.
- Market Makers: Market makers are firms or individuals who ensure liquidity in the stock market by continuously buying and selling stocks. They provide both buy and sell prices for a stock, ensuring that there’s always a market for investors to trade. Without market makers, stocks would be less liquid, making it harder to buy or sell shares at fair prices.
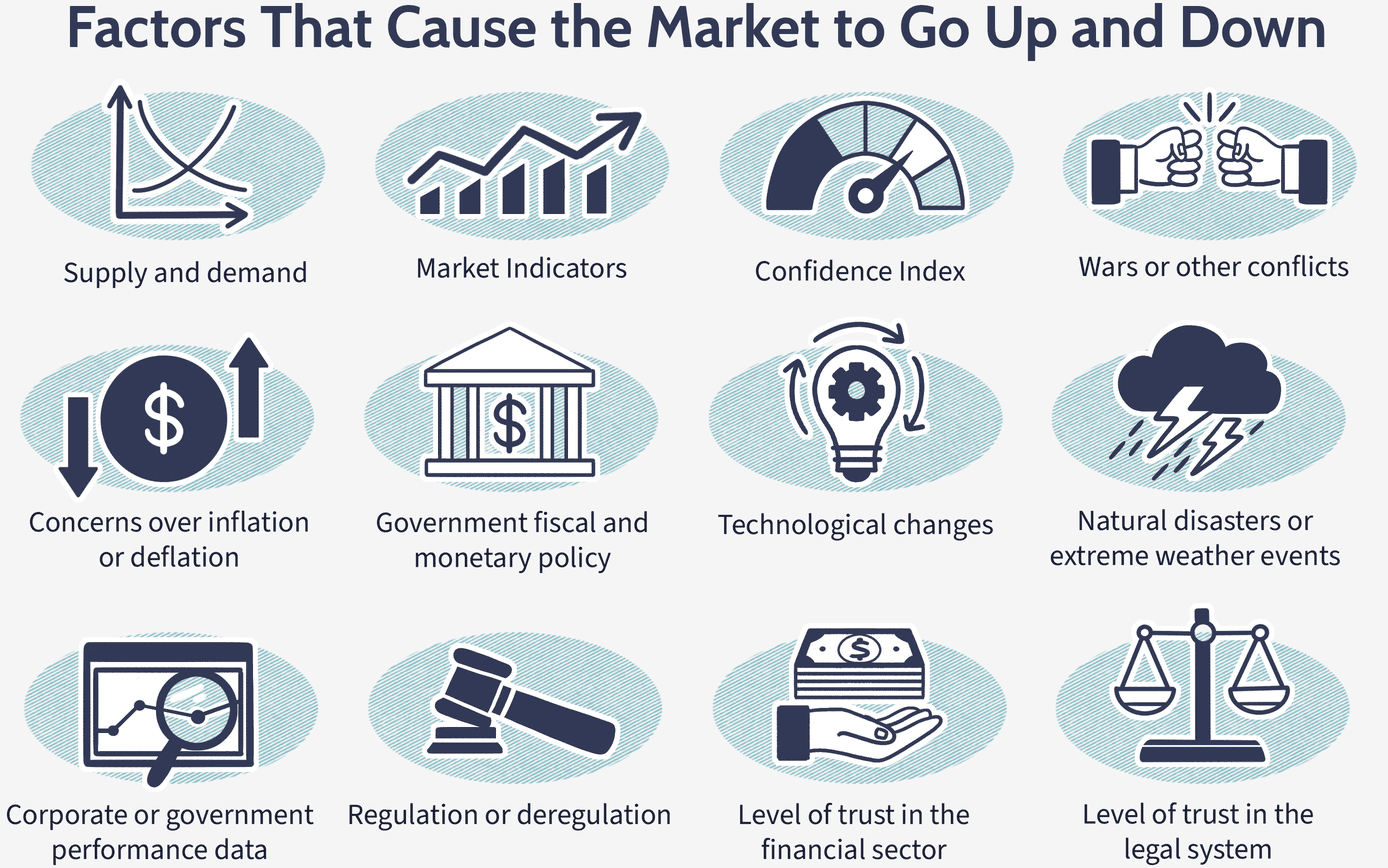
Factors Influencing Stock Prices
Stock prices fluctuate due to various factors, making the stock market unpredictable in the short term.
- Company Performance: A company’s earnings reports, product launches, or management changes can cause its stock price to rise or fall. Strong financial performance generally leads to higher stock prices, while poor performance can lead to declines.
- Economic Indicators: Broader economic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and employment rates, also affect stock prices. For instance, if the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, which can boost corporate profits and lead to higher stock prices.
- Market Sentiment: Sometimes, stock prices are driven by investor psychology rather than fundamentals. For example, fear of a recession may cause stock prices to fall, even if a company’s financials are strong. Conversely, optimism about future growth can push stock prices up.
Stock Market Regulation and the Role of the SEC
The stock market is regulated by government agencies to ensure fair trading and protect investors from fraud.
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): The SEC is the primary regulatory body overseeing the U.S. stock market. Its role is to ensure that companies provide accurate financial information and that all investors have access to this information. The SEC also enforces laws to prevent insider trading and other illegal practices.
- Market Regulation: Stock exchanges and brokers are also subject to rules that ensure transparency and fairness in trading. For example, public companies must file quarterly earnings reports, and stock exchanges monitor for unusual trading activity that may indicate market manipulation.
What is stock market: Long-Term vs. Short-Term Investing
When learning how the stock market works, it’s important to understand the difference between long-term and short-term investment strategies.
- Long-Term Investing: Long-term investors buy stocks intending to hold them for years or even decades. The stock market has historically trended upward over the long term, making this a strategy that typically builds wealth slowly but steadily.
- Short-Term Trading: In contrast, short-term trading involves buying and selling stocks over days, weeks, or months to capitalize on market volatility. While this approach can generate quick profits, it also carries more risk and requires more active management.
How Investors Make Money in the Stock Market
Investors typically make money in the stock market in two main ways—capital gains and dividends.
- Capital Gains: When you buy a stock at a low price and sell it at a higher price, you make a profit called a capital gain. For example, if you buy a stock at $50 and sell it at $70, your capital gain is $20 per share.
- Dividends: Some companies pay dividends to shareholders, which are portions of the company’s profits distributed regularly (usually quarterly). Dividends provide an additional source of income and can be reinvested to buy more shares.
What is Stock Market Role
The primary function of the stock market is to allow companies to raise capital by issuing shares to investors. Investors, in turn, can buy, sell, or trade these shares to profit from changes in stock prices or to receive dividends.
- Capital Raising: Companies use the stock market to raise capital by selling shares to the public. This process, called an Initial Public Offering (IPO), provides companies with the funds they need for expansion, research, or operations.
- Wealth Building: For investors, the stock market offers an opportunity to build wealth through price appreciation and dividends. Over time, investors can grow their portfolios by holding shares in companies that increase in value or distribute profits as dividends.
- Economic Growth: A thriving stock market is often a sign of a healthy economy. When businesses grow and profit, it boosts overall economic productivity. In turn, this creates jobs, increases consumer spending, and generates wealth for shareholders.
Sources:
- https://www.sec.gov/
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/basics/06/invest1000.asp
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/stockmarket.asp
- https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/082614/how-stock-market-works.asp
- https://www.dowjones.com/smartmoney/what-is-the-stock-market/
- https://www.forbes.com/advisor/in/investing/what-is-stock-market/