Nvidia announced it is investing $5 billion to acquire common stock in Intel at $23.28 per share. Intel will issue new shares, making Nvidia one of its largest shareholders.
They plan to jointly develop next-generation chips for AI data centers and PCs, integrating Nvidia’s AI/accelerated computing stack with Intel’s CPUs and the x86 ecosystem. The deal does not include Intel’s foundry business in this collaboration. Nvidia won’t outsource its chip manufacturing to Intel under this agreement.
Why It Matters
Intel gets a lifeline: Intel has been underperforming lately, with expenses rising, losses mounting, and stiff competition in the AI chip market. This deal gives Intel both cash and credibility.
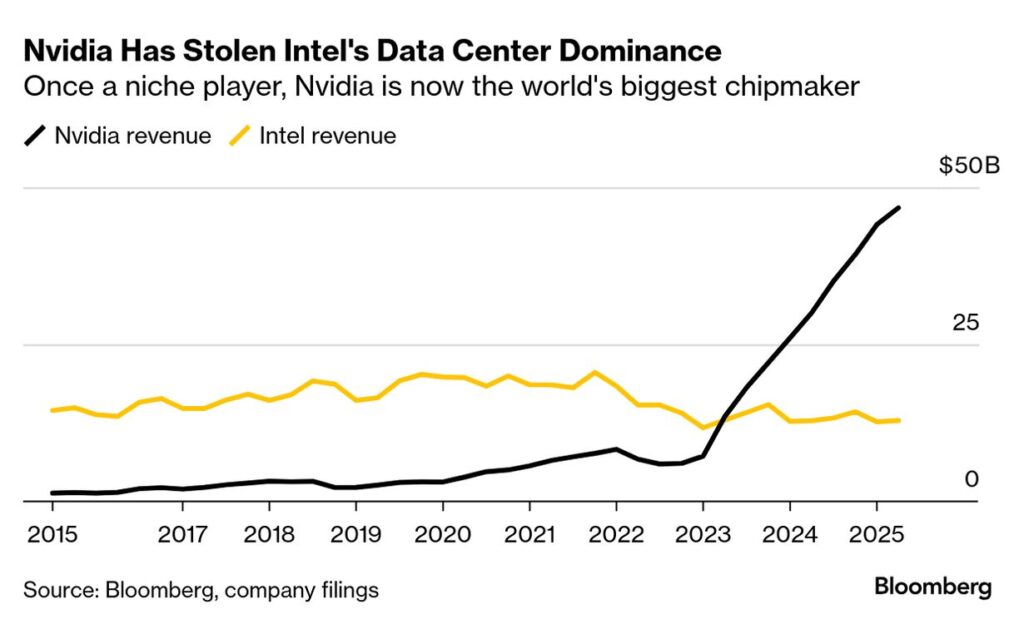
Strategic win for Nvidia: By tying with Intel, Nvidia gets deeper integration with CPU infrastructure, potentially improving performance for AI systems that need CPU-GPU communication (data centers, HPC, etc.). Also, using Intel’s CPU base plus Nvidia’s GPU strength may create competitive pressure on rivals like AMD and others.
Policy and national tech push: The U.S. government recently took a 10% stake in Intel to support domestic chip manufacturing. This deal aligns with broader policy goals to reduce dependence on foreign suppliers and ensure U.S. leadership in semiconductor technology.
Market Reaction
- Intel stock: Jumped roughly 30% in premarket trading after the announcement.
- Nvidia stock: Increased modestly (~3%) — less dramatic move, since Nvidia is the investing party rather than the rescued one.
The Big Picture & Risks
| Area | Upside | Risks / Questions |
|---|---|---|
| Technology & Competitive Position | Combines Nvidia’s AI GPU strength with Intel’s CPU and existing x86 base; potential innovations in AI architectures, better CPU-GPU interconnects. | Intel’s foundry business remains weak; no guarantee Nvidia will source its chips from Intel’s foundries. Execution risk, regulatory approvals, and integration complexity. |
| Financial & Market | Boosts Intel’s valuation, investor confidence; may shift industry dynamics (AMD, others may feel pressure). Nvidia gets broader CPU/GPU platform leverage. | Dilution risk for Intel shareholders; Intel has been losing ground in various segments; Nvidia’s regulatory risk (both antitrust and export) especially in U.S.-China context. |
| Policy / Geopolitics | Aligns with U.S. goals for chip independence; increases domestic chip R&D and production credibility. | Trade tensions, export restrictions, China’s response, and regulatory scrutiny could limit impact. Also Intel must deliver innovation and cost efficiency. |
What to Expect Next
- Intel and Nvidia will likely roll out prototype or early versions of joint PC/AI products in the coming quarters. Keep an eye out for announcements of new CPU+GPU designs, especially those focused on “high-communication” between CPU and GPU.
- Watch for competitor reaction: AMD, Broadcom, and others are likely to respond, either by accelerating their own partnerships or pushing for more product innovation.
- Regulatory scrutiny: Given government interest in semiconductors and national security, this deal may undergo review. Export rules and trade relations (especially with China) could impact how much of the product collaboration can be commercially realised.
- Financial performance: Intel has to improve margins; Nvidia’s return is likely more strategic than purely financial in the short term.
This Nvidia-Intel deal is more than just a big check, it’s a bet that cooperation, not only competition, may define the next era of the AI computing race. Intel gets a much-needed boost; Nvidia secures stronger CPU integration; the tech landscape shifts. But execution, regulatory hurdles, and global trade headwinds will test how much value actually comes out of this.
Disclosure: This article does not represent investment advice. The content and materials featured on this page are for educational purposes only.