Cryptocurrency mining is the process of verifying and adding transactions to a blockchain, a decentralized digital ledger. In simple terms, mining is how new coins are created in certain cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, and when they solve these problems, they earn the right to add a new block of transactions to the blockchain. For their efforts, miners are rewarded with newly minted cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum.
Mining is essential to maintaining the security and decentralization of the blockchain. Without it, there would be no mechanism to verify transactions or prevent fraud in cryptocurrency networks.

How Does Cryptocurrency Mining Work?
Cryptocurrency mining works through a combination of technologies and concepts, such as transactions, blockchain, hash functions, and proof of work. Here’s a breakdown of how it operates:
- Transactions: Each time a cryptocurrency transaction takes place, such as sending Bitcoin from one person to another, it gets broadcast to the network. These transactions are collected into blocks that need to be validated and added to the blockchain.
- The Digital Ledger and Blockchain: A blockchain is a digital, decentralized ledger that records all transactions made in a cryptocurrency network. It ensures transparency and security. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered.
- Hash Functions: Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic algorithms called hash functions. These functions take transaction data and convert it into a fixed-length string of numbers and letters. This process, called hashing, is crucial because it ensures the integrity of the blockchain. If any detail of a transaction is changed, the hash will change, revealing that tampering has occurred.
- Proof of Work (PoW): To add a block to the blockchain, miners must solve a complex mathematical puzzle through proof of work (PoW). This involves generating a hash that matches the conditions set by the network, which requires immense computational power. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the block to the chain and earns a cryptocurrency reward.
- Validation: Once the block is added, other miners and nodes in the network validate the block to ensure the transactions are legitimate and that no double-spending has occurred.
Tools and Equipment Needed for Cryptocurrency Mining
To start cryptocurrency mining, you’ll need specialized hardware and software, as well as a few additional tools to make the process smoother.
- Mining Hardware: The type of hardware you need depends on the cryptocurrency you’re mining. For Bitcoin, specialized ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) are commonly used because they are designed solely for Bitcoin mining and are far more efficient than GPUs. For altcoins like Ethereum, GPUs (Graphics Processing Units) are still widely used.
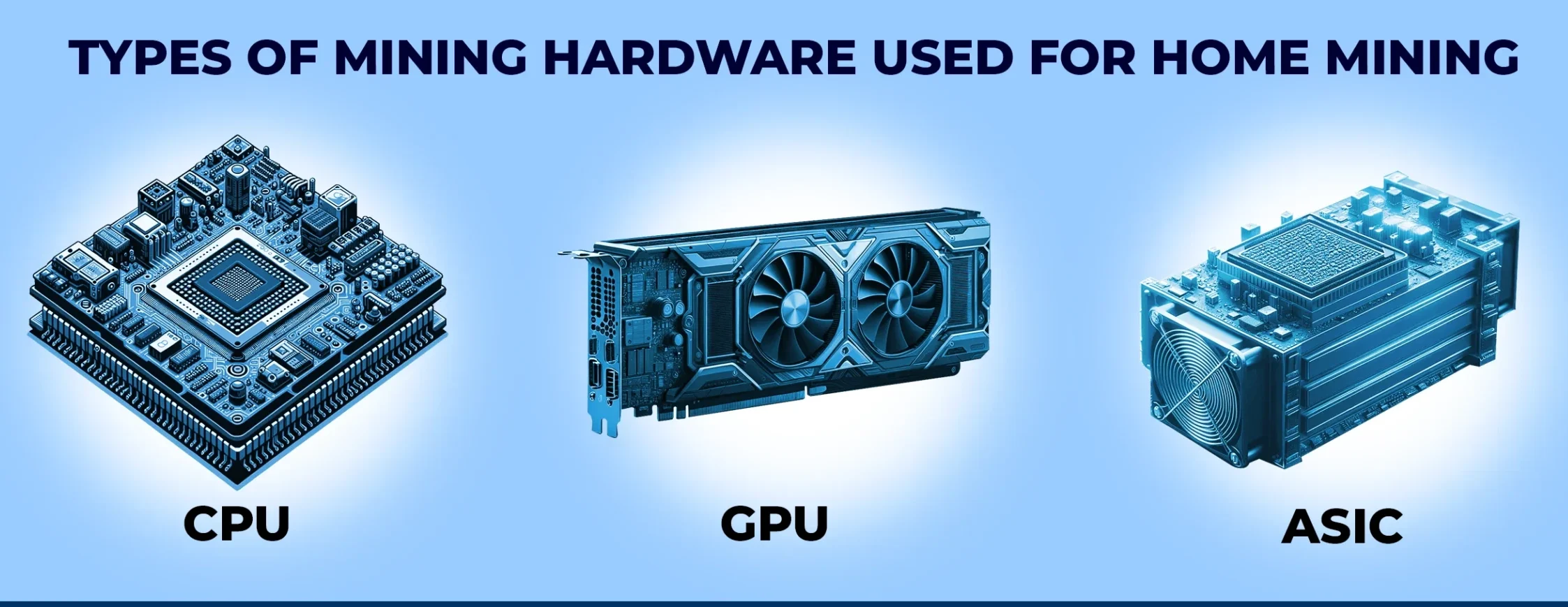
- Mining Software: Once you have the hardware, you need software to connect your rig to the blockchain. Popular options include CGMiner, EasyMiner, and NiceHash. This software monitors your hardware and manages the mining process.
- Wallet: A cryptocurrency wallet is essential to store the coins you mine. Wallets can be either hardware (physical devices) or software-based. It’s critical to choose a secure wallet, as your earnings need to be protected from theft and hacking.
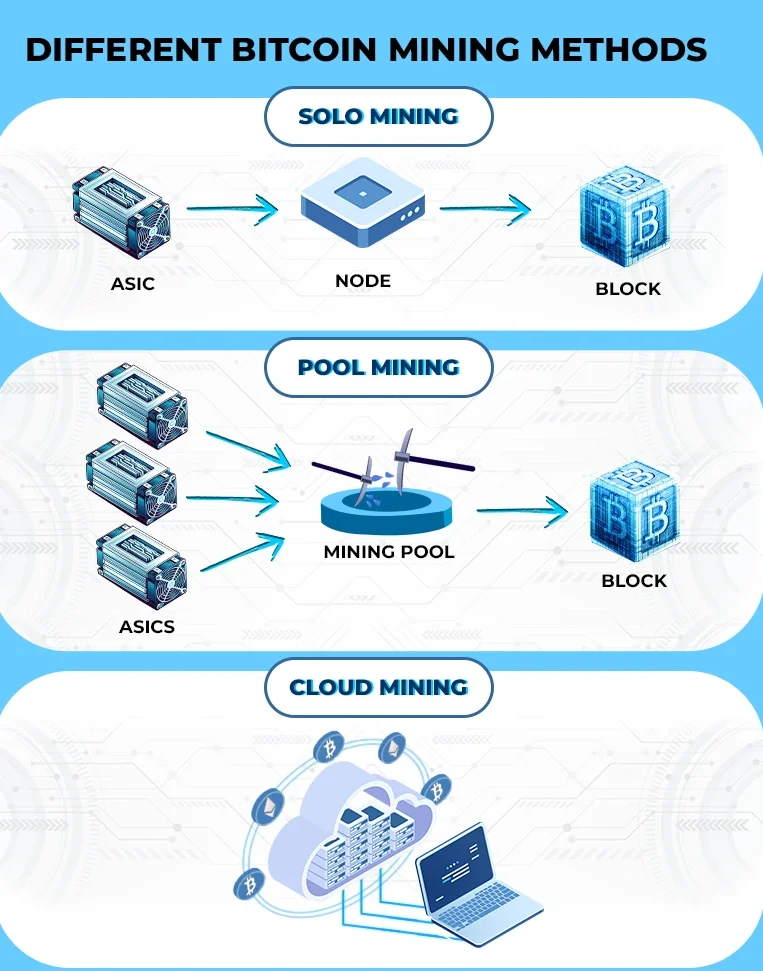
- Mining Pool: For beginners, mining solo can be unprofitable due to the high competition. A mining pool allows miners to pool their resources and share rewards based on the computational power they contribute. Popular pools include Slush Pool and F2Pool
7 Methods of Crypto Mining
Cryptocurrency mining can be done in various ways, depending on the type of cryptocurrency you’re mining and your available resources. Below are seven common methods:
- ASIC Mining (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit Mining)
This mining is a specialized form of mining that uses custom-built hardware designed to mine specific cryptocurrencies, primarily Bitcoin. ASIC miners are highly efficient and fast, but they are expensive and only useful for mining certain coins. - GPU Mining (Graphics Processing Unit Mining)
GPU mining uses high-end graphics cards to mine cryptocurrencies. This method is more versatile than ASIC mining because GPUs can mine a wide variety of coins, including Ethereum and altcoins. It’s a popular option for both beginners and experienced miners. - CPU Mining (Central Processing Unit Mining)
CPU mining uses your computer’s central processor to mine cryptocurrency. While this method was common in the early days of Bitcoin, it is now slow and less profitable due to advancements in hardware and increasing mining difficulty. CPU mining is mostly used for smaller or privacy-focused cryptocurrencies like Monero. - Cloud Mining
Cloud mining allows you to rent mining hardware or computing power from a service provider. Instead of setting up your own mining rig, you pay a subscription or rental fee to mine cryptocurrency through a remote data centre. The provider takes care of the hardware maintenance, electricity, and other operational costs. - FPGA Mining (Field-Programmable Gate Array Mining)
FPGA mining uses a type of hardware that can be programmed to mine different cryptocurrencies. It’s more flexible than ASICs but generally less powerful. FPGAs offer a balance between efficiency and versatility, making them suitable for multiple coins. - Mobile Mining
Mobile mining uses smartphones to mine cryptocurrencies through mobile apps. While accessible, this method is highly inefficient and not recommended for serious mining due to the limited processing power and potential to overheat and damage devices. - Solo mining
Solo mining is s when an individual miner works independently, trying to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain without joining a mining pool. All the mining rewards go to the miner who successfully solves the cryptographic puzzle first. This method was more common in the early days of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, but it’s now mostly used by experienced miners with access to significant computational resources or those mining smaller, less competitive cryptocurrencies.
Profitability and Risks of Crypto Mining
Is cryptocurrency mining profitable? The answer depends on several factors, such as the cryptocurrency you’re mining, electricity costs, and the efficiency of your hardware.
- Profitability: To assess whether mining is profitable, you need to calculate the cost of electricity in your area, hardware efficiency, and the cryptocurrency’s market price. Tools like WhatToMine help miners estimate their potential earnings.
- Risks: The major risks of cryptocurrency mining include fluctuating market prices, high electricity costs, and the risk of hardware becoming obsolete. There’s also the chance of government regulations or outright bans in some regions
Legal Status of Cryptocurrency Mining
Cryptocurrency mining is legal in most countries, but some have imposed bans or strict regulations due to environmental concerns and energy consumption.
- Countries that have banned mining:
- China: In 2021, China completely banned cryptocurrency mining, citing environmental concerns and financial risks.
- Iran: The government has intermittently banned mining to alleviate stress on the country’s electricity grid, particularly during peak summer months.
- Bolivia: Cryptocurrency mining, along with all cryptocurrency-related activities, is banned in Bolivia.
- Countries with regulated mining:
- United States: Mining is legal but subject to state-level regulations. Some states, like New York, have proposed stricter guidelines due to environmental concerns.
- Russia: Mining is legal but not regulated extensively. However, the government is considering tighter control over mining operations.
- Kazakhstan: After China’s ban, many miners relocated to Kazakhstan, which became one of the leading hubs for Bitcoin mining. The country has imposed some regulations to control energy use.
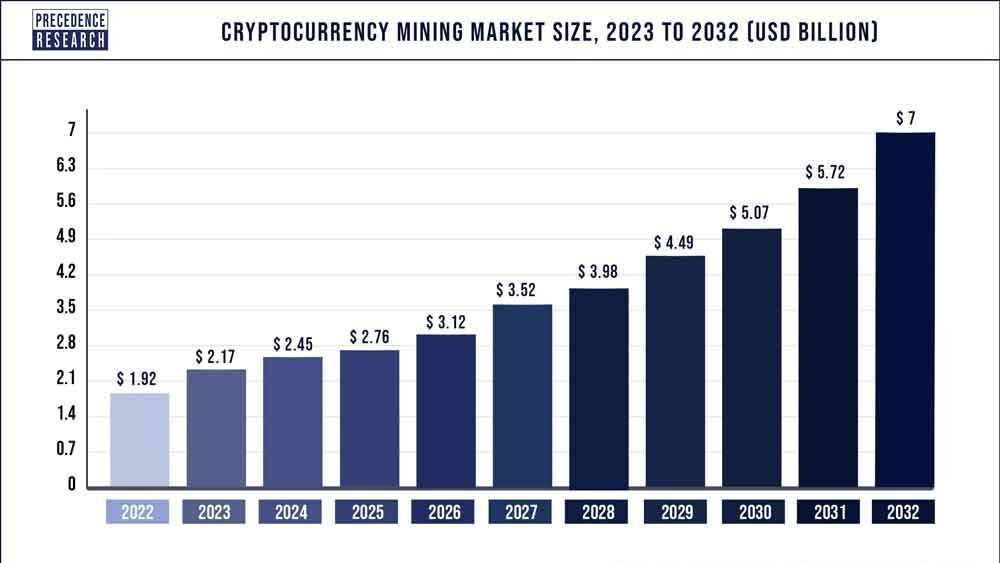
Future of Cryptocurrency Mining
The future of cryptocurrency mining is likely to evolve with advancements in technology and energy solutions. Two significant developments include:
- Shift to Proof of Stake (PoS): Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency, is transitioning from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS), which eliminates the need for energy-intensive mining. Other cryptocurrencies may follow suit, reducing the demand for mining hardware and energy.
- Sustainable Mining: With growing concerns about the environmental impact of mining, more companies are exploring green mining solutions. These include using renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower to run mining operations, particularly in regions with abundant natural resources.
Cryptocurrency mining will continue to be a key aspect of blockchain networks, but the landscape is changing. Miners will need to adapt to technological advances and evolving regulatory environments to remain profitable and sustainable.
Sources:
- https://www.investopedia.com/tech/how-does-bitcoin-mining-work/
- https://cointelegraph.com/learn/how-to-mine-bitcoin-a-beginners-guide-to-mine-btc
- https://medium.com/@dx25labs/the-beginners-guide-to-crypto-mining-92f3fa67cc32
- https://www.inx.co/learn/beginners/crypto-mining-a-beginners-guide-to-earning-passive-income/